Research Interests
Dr. Gong’s research interests span visual computing, including computer graphics, computer vision, image processing, and pattern recognition. To date, he has published over 160 refereed technical papers, including 25 in ACM/IEEE Transactions. He has received the 2025 SIGGRAPH Test-of-Time Award as well as multiple best-paper awards with his students.
His publications are indexed by Google Scholar, DBLP, ORCID, ResearchGate, ACM Portal, and IEEE Xplore. For a complete publication list, please refer to his Curriculum Vitae.
Selected Research Topics
Here are several key research topics and related publications from Dr. Gong’s work.
Computer Graphics and Visualization

Architectural Programs for Structured 3D Abstraction
We present ArcPro, a learning framework that reconstructs structured 3D buildings from sparse, noisy point clouds using architectural programs. A domain-specific language encodes hierarchical structures, while an encoder–decoder network predicts programs for efficient and faithful reconstruction.
Papers: CVPR 2025
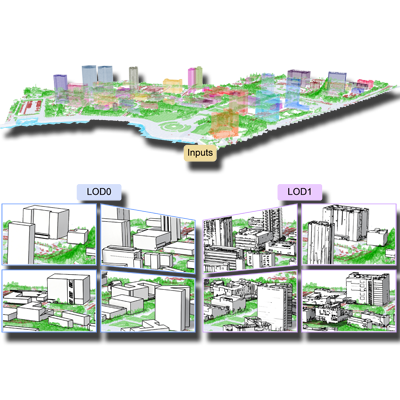
Architectural LOD Generation
We aim to generate structured and semantically consistent level-of-detail (LOD) representations for large-scale 3D urban and architectural models. By analyzing geometric primitives and their spatial relationships, the methods produce hierarchical LOD structures that support efficient visualization and meaningful abstraction.
Papers: JPRS 2025, SIGGRAPH Asia 2024

Generalized Cylinder Decomposition
We present an optimization framework for decomposing complex shapes into generalized cylindrical parts. By defining cylindricity as a compact geometric measure based on skeletal and profile representations, our method progressively constructs and globally optimizes cylinder covers to achieve meaningful, geometry-aware decompositions.
Papers: SIGGRAPH Asia 2015

Projective Analysis for 3D Shape Segmentation
We propose projective analysis for semantic segmentation and labeling of 3D shapes by leveraging knowledge from labeled 2D images. By analyzing and fusing multiple labeled projections, the method enables robust labeling of incomplete or imperfect 3D models through efficient, topology-aware matching in image space.
Papers: SIGGRAPH Asia 2013
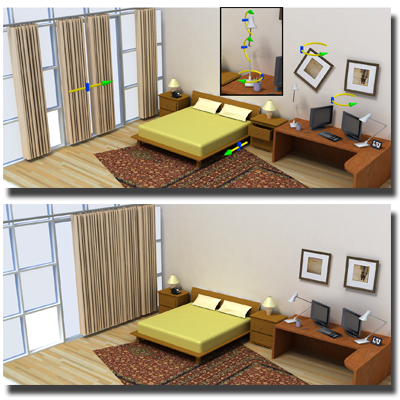

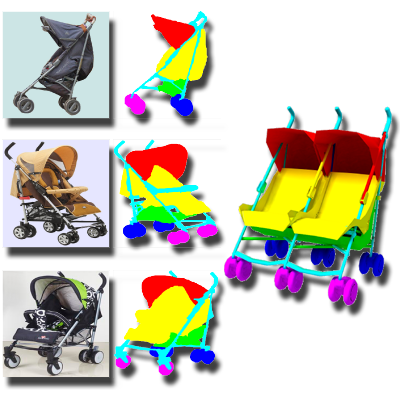
Mobility Trees for Indoor Scene Manipulation
We present the mobility-tree, a hierarchical representation that captures object motion and functional relationships in complex 3D indoor scenes. By analyzing object repetition and spatial relations, it enables intuitive, high-level scene manipulation and editing.
Papers: CGF 2013
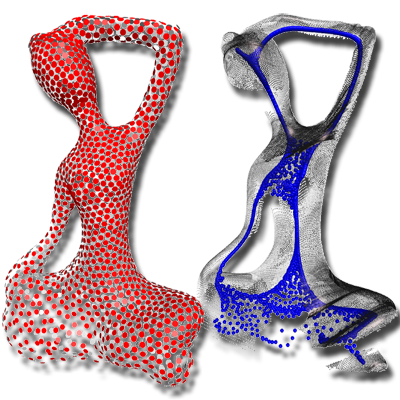
Deep Points Consolidation
We propose a deep points representation for consolidating noisy point clouds, where each surface point is paired with an inner skeletal point. A joint optimization aligns these pairs with surface normals, enabling effective geometry completion and noise removal.
Paper: SIGGRAPH Asia 2015
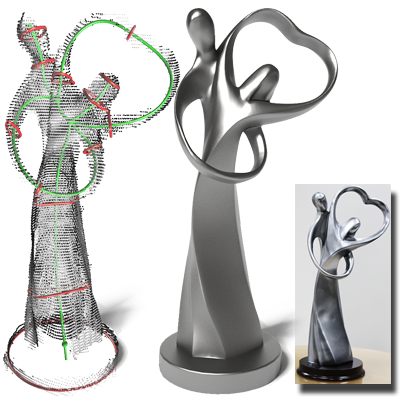

Reconstruction from Incomplete Point Clouds
We propose an interactive method for reconstructing surfaces from sparse point scans with sharp features. Users edit skeletal and profile curves, while a morph-to-fit scheme interpolates and aligns the surface to produce accurate, feature-preserving reconstructions.
Paper: SIGGRAPH Asia 2014
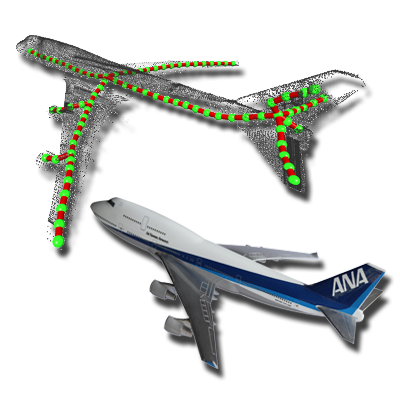

L1-Medial Skeleton of Point Clouds
We introduce the L1-medial skeleton, a robust curve-skeleton representation for 3D point clouds. By locally adapting L1-medians, our method extracts 1D skeletal structures directly from noisy, incomplete scans without requiring surface normals or topology assumptions.
Paper: SIGGRAPH 2013
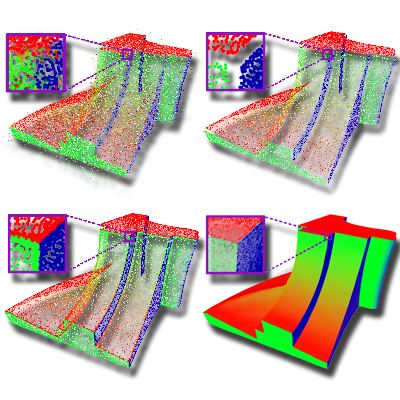
Edge-Aware Point Set Resampling
We propose Edge-Aware Resampling (EAR), a method for consolidating noisy point clouds while preserving sharp features. By resampling away from edges to estimate reliable normals and progressively refining near singularities, EAR produces clean, noise-free normals and improves subsequent reconstruction and rendering quality.
Paper: TPAMI 2017, TOG 2013
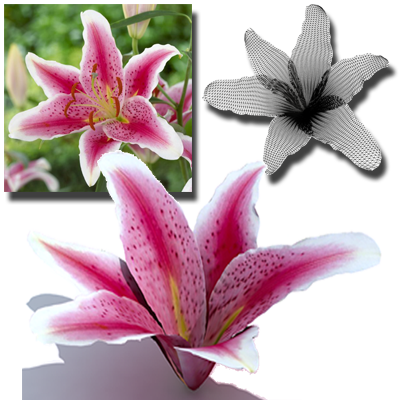

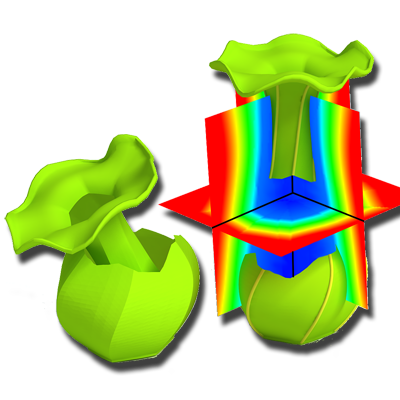
3D Flower Reconstruction
We developed 3D reconstruction techniques for flowers, addressing the challenges of thin, overlapping petals and complex deformations. A static flower model can be generated from a single photograph, while dynamic blooming sequences are reconstructed from time-varying 4D point clouds.
Papers: CGF 2017, Eurographics 2014
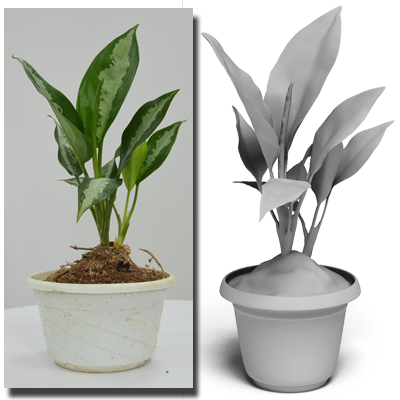

Intrusive Plant Acquisition
We propose a technique for 3D acquisition and modeling of plants using an intrusive approach that disassembles specimens for precise scanning. A global-to-local non-rigid registration method then reassembles the parts into complete, structurally consistent models.
Papers: CGF 2016
Field-Guided Registration for Shape Composition
We propose an automatic shape composition method that seamlessly fuses non-overlapping parts with sharp or distinct features. Using a feature-conforming field-guided registration, the method aligns and blends parts through surface-to-field matching and smooth gap interpolation.
Papers: SIGGRAPH Asia 2012
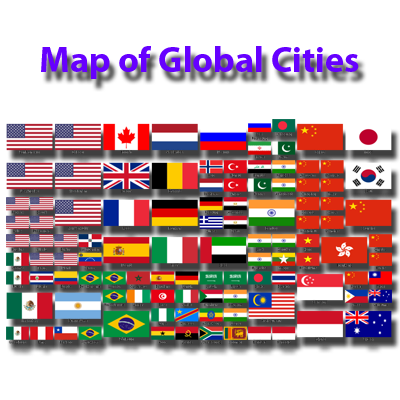
Organizing Data into Structured Layouts
We present the Self-Sorting Map (SSM), an algorithm that organizes data into a structured, non-overlapping layout where similar items are placed close together. Combining ideas from dimensionality reduction, sorting, and clustering, SSM transforms optimization into a discrete labeling task, enabling fast and intuitive visualization of large datasets.
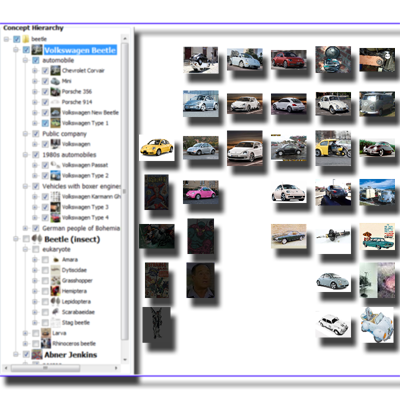
Concept-Based Web Image Search
We propose an image retrieval approach that uses Wikipedia-based query expansion to generate diverse results for ambiguous searches. By combining conceptual and visual organization, the system enables users to explore, filter, and refine results for improved precision and relevance.
Papers: IP&M 2013, JAIHC 2013, JETWI 2012
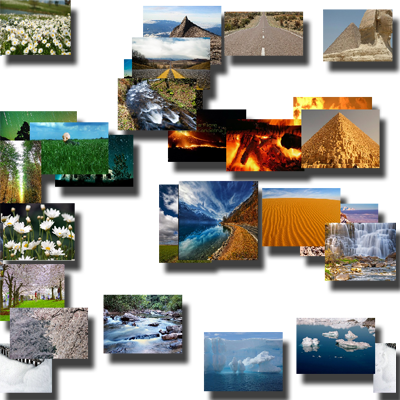

Similarity-Based Image Browsing
We present a GPU-accelerated algorithm for organizing and browsing large image collections by visual similarity on a 2D canvas. By extracting color and gradient features and mapping them via a self-organizing map, the system enables smooth, intuitive exploration of related images through simple pan and zoom interactions.
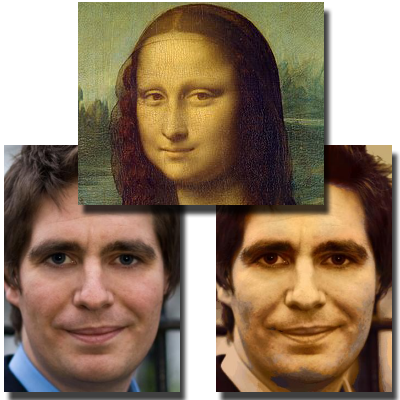

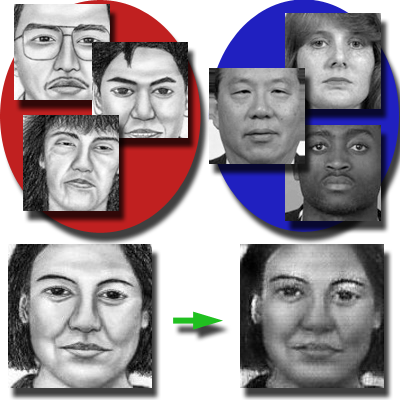
Face Photo Synthesis
We explore face photo synthesis through both rule-based and learning-based approaches. These methods demonstrate how guided modeling and exemplar-driven transfer can generate high-quality, visually coherent face edits across diverse styles and age ranges while preserving identity.
Papers: AppIntell 2023, TVCJ 2017
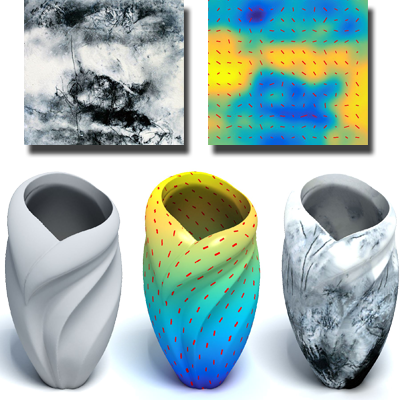
Controlled Synthesis of Inhomogeneous Textures
We propose a method for analyzing and synthesizing complex inhomogeneous and anisotropic textures. By deriving a guidance map that encodes spatial progression and local orientation from an input exemplar, the approach enables controlled texture synthesis with realistic spatial and directional variation.
Papers: Eurographics 2017
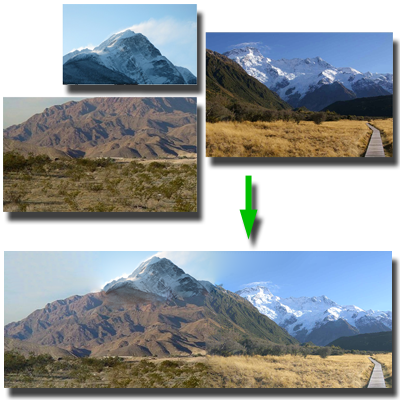

Structure-Driven Image Completion
We propose a method for assembling non-overlapping image fragments into a coherent composition without prior positional information. Using salient curve correspondences to guide a tele-registration process, the approach aligns all pieces simultaneously and fills gaps through structure-driven completion for seamless reconstruction.
Papers: SIGGRAPH Asia 2013
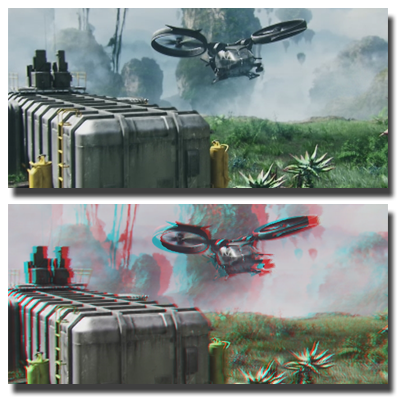

Video Stereolization
We present a semiautomatic system for converting 2D videos into stereoscopic ones using motion analysis and minimal user input. Combining structure-from-motion with optical flow–based depth cues, it efficiently generates dense, high-quality depth maps for mono-to-stereo conversion.
Papers: TVCG 2012
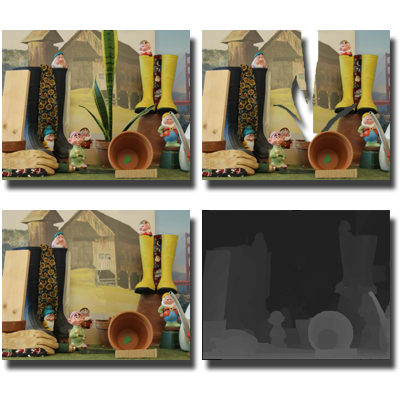

Stereoscopic Inpainting
We propose an algorithm for simultaneous color and depth inpainting using stereo image pairs and disparity maps. By combining segmentation-based disparity completion, mutual 3D warping, and depth-guided texture synthesis, the method effectively restores missing regions caused by occlusion or object removal.
Papers: CVPR 2008

Renderability for Image-Based Rendering
This work introduces renderability, a metric that predicts IBR quality for any viewpoint and direction and guides viewpoint and path selection. Two VR applications—a path planner and a view selector—demonstrate how this concept supports interactive navigation and high-quality scene exploration in large-scale environments.
Papers: IEEE VR 2023
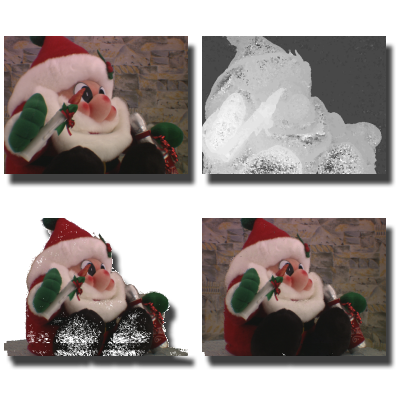
Camera Field Rendering
We propose backward disparity-based rendering methods that synthesize novel views from sparse inputs without dense depth or geometry. Using backward search and disparity-guided interpolation, the approach achieves robust, high-quality rendering of dynamic scenes in real time.

Taxonomy for Image-Based Rendering
We introduce the rayset concept—a parametric function mapping to both ray and attribute spaces—as a unified framework for image-based rendering. Under this formulation, existing scene representations and reconstruction methods can be interpreted as variations or transformations of raysets.
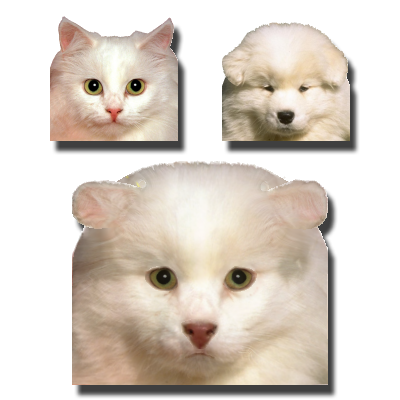

Layer-Based Morphing
We introduce novel morphing approaches to address ghosting and visibility issues in traditional image morphing. By morphing regions independently and organizing them into layers, the methods enable separate object control and recover hidden information for smoother, more realistic transitions.
Papers: GM 2001
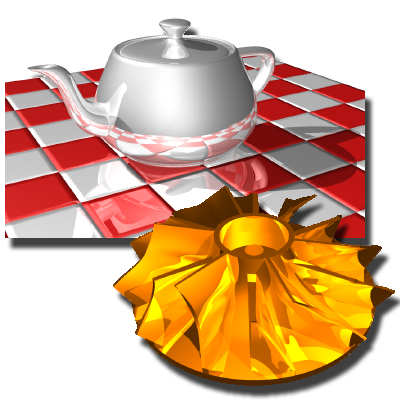

Fast Ray–NURBS Intersection Calculation
We present an efficient ray–surface intersection method for NURBS models that accelerates Newton iteration using polynomial extrapolation. Defining rays via non-orthogonal planes and enclosing patches with tight trapezoid prisms reduces computation, enabling faster and more reliable ray tracing.
Papers: C&G 1997
Computer Vision

Class-Agnostic Object Counting
We study class-agnostic object counting with an emphasis on zero-shot generalization, reducing reliance on manually provided exemplars while supporting arbitrary object categories. By learning exemplar cues from language guidance or visual self-similarity, these approaches enable accurate counting across diverse scenes with minimal supervision.
Papers: PR 2026, PR 2024
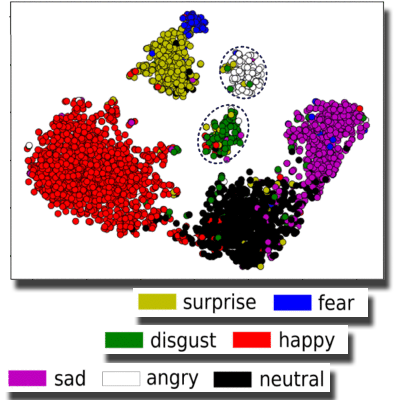
Facial Expression Recognition
We advance facial expression recognition (FER) through improved feature representation and multimodal supervision. By combining hybrid architectures with discriminative feature disentanglement, our approach captures subtle expression differences while reducing identity bias for superior real-world performance.
Papers: TMM 2025, InfSci 2022
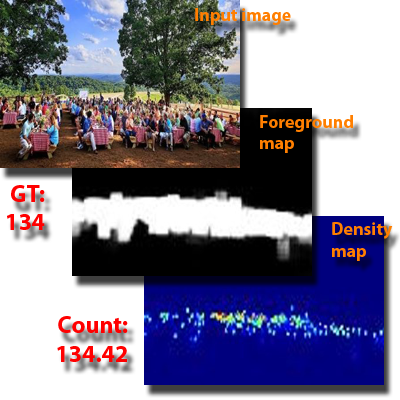
Learning-Based Crowd Counting
We propose novel machine learning frameworks for crowd counting that enhance generalization and efficiency under limited supervision. Using multi-granularity modeling, hierarchical scale learning, and scale-invariant transformations, they robustly capture global dependencies and adapt to diverse crowd densities.
Papers: WACV 2023, PR 2023, TMM 2023, Neurocomputing 2021
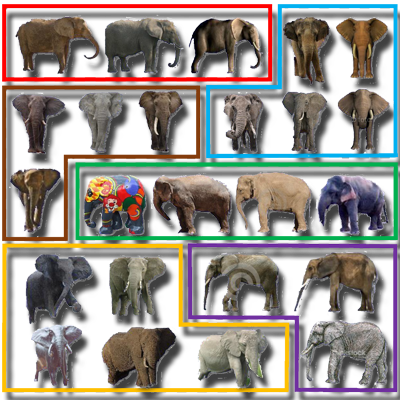
Distilled Collections from Textual Image Queries
This paper introduces an unsupervised distillation algorithm that extracts clean, coherent subsets of relevant images from large, noisy internet collections. By clustering loosely segmented foreground shapes rather than entire images, the method jointly achieves object distillation and segmentation without semantic supervision.
Papers: Eurographics 2015
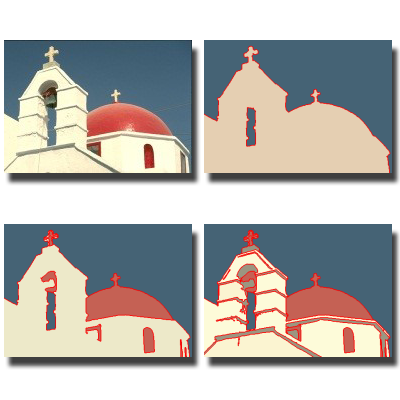

Multilevel Image Segmentation using Fuzzy Entropy
We improve multilevel image segmentation based on fuzzy c-partition entropy by enhancing efficiency, smoothness, and applicability. These methods achieve unsupervised, accurate, and efficient segmentation for both grayscale and color images, outperforming traditional threshold-based techniques.
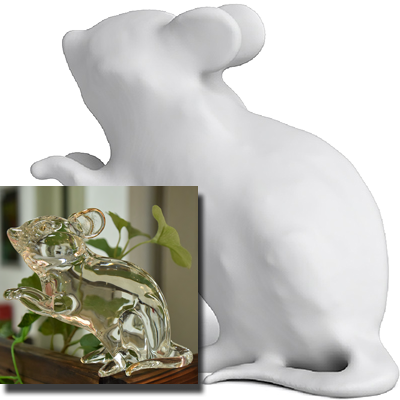

Transparent Object Modeling
We tackle the challenging problem of reconstructing transparent objects, where traditional 3D methods fail due to light refraction. We leverage physical modeling of refraction and normal consistency to jointly recover surface geometry and shape details.
Papers: SIGGRAPH 2018, CVPR 2016
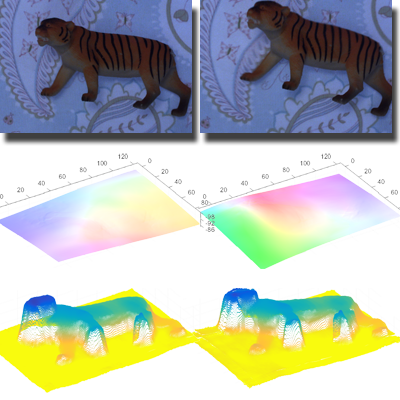
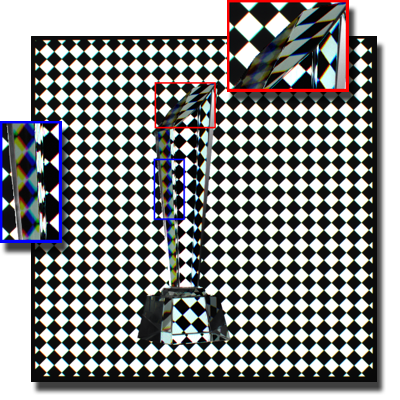
Water Surface Reconstruction
We reconstruct 3D structures of scenes involving refractive water surfaces by leveraging physical constraints from light refraction. The core idea is to enforce consistency between surface normals derived from Snell’s law and those estimated from local geometry to achieve accurate reconstruction.
Frequency-Based Environment Matting
This paper presents an efficient approach for capturing and extracting environment mattes based on frequency analysis and compressive sensing. By incorporating phase information into the acquisition process, the method accurately identifies light contributions while significantly reducing capture and computation time.
Papers: ICCV 2015
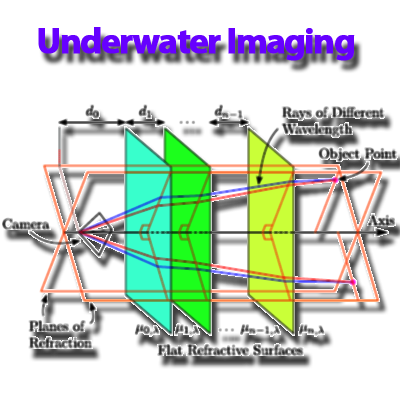
Underwater Camera Calibration
This paper introduces an improved underwater camera calibration method that accounts for light dispersion in refraction modeling. By deriving new physical constraints on model parameters and employing a custom calibration device, the approach achieves higher accuracy than existing techniques.
Papers: CVPR 2013
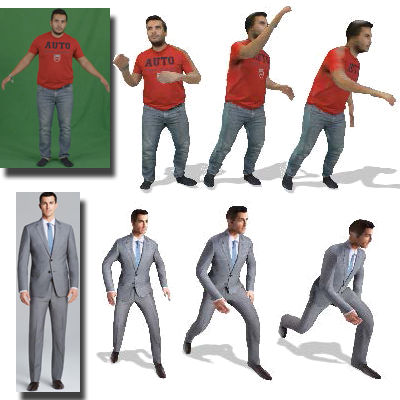

Conditioned Generation of 3D Human Motions
We address the challenge of generating realistic and diverse human motion sequences conditioned on action categories. By integrating 3D motion synthesis with video rendering, the approaches produce natural, multi-view human action sequences that outperform existing methods in realism and variability.
Papers: IJCV 2022, ACM MM 2020
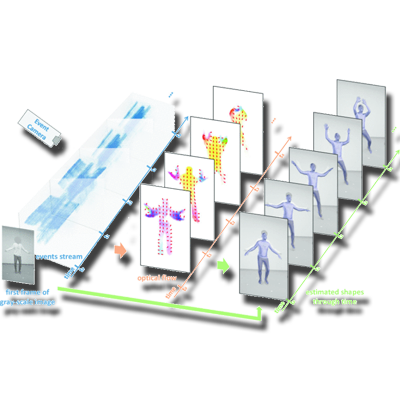
Event-based 3D Human Pose and Shape Estimation
We present EventHPE, a two-stage framework for estimating 3D human pose and shape from event camera data. By jointly leveraging event-based motion cues and learned optical flow with a flow coherence loss, EventHPE achieves accurate dynamic human reconstruction from sparse event signals.
Papers: ICCV 2021
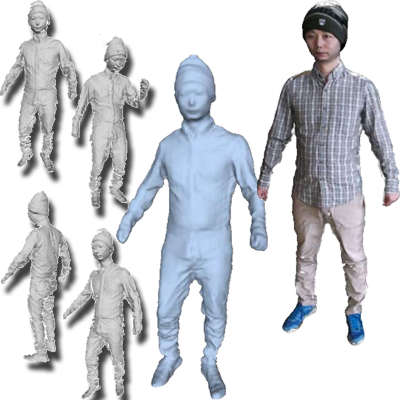

Human Avatar Modeling from Sparse RGBD Images
This paper presents a framework for reconstructing complete 3D human body models from sparse RGBD frames captured by a single moving camera. By combining pairwise alignment with global non-rigid registration guided by a generative human template, the method robustly handles pose variation and occlusion.
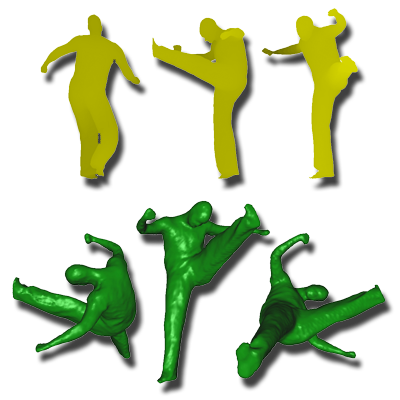

Modeling of Deformable Human Shapes
This paper presents a method for reconstructing complete 3D deformable surfaces over time using a single depth camera. Assuming smooth, continuous motion, the algorithm aligns and merges partial reconstructions from different frames through mesh warping and volumetric fusion.
Papers: ICCV 2009
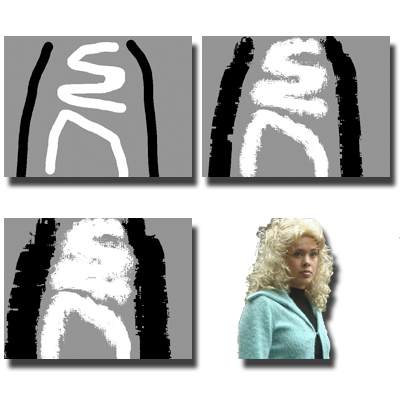
Foreground Segmentation for Live Videos
This paper introduces a foreground segmentation algorithm designed for live videos with complex backgrounds and fuzzy object boundaries. It employs two competing one-class SVMs per pixel to model local color distributions of the foreground and background, enhancing discrimination and boundary handling.
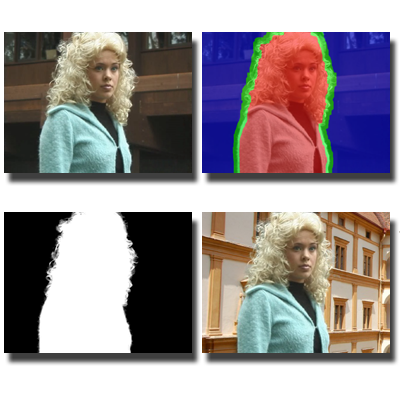

Real-Time Video Matting
We develop a real-time video matting system that fuses color and depth information to achieve precise foreground extraction. Using Poisson-based matting equations designed for multichannel color and depth cues, the system delivers high-quality results under diverse lighting and motion conditions.
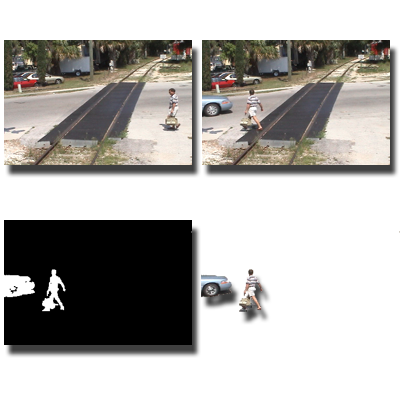

Background Subtraction from Dynamic Scenes
We develop real-time algorithms for foreground segmentation and moving object detection in videos with dynamically changing backgrounds. By formulating the task as minimizing a constrained risk functional within an online learning framework, our approach adapts efficiently to both temporal and spatial variations.
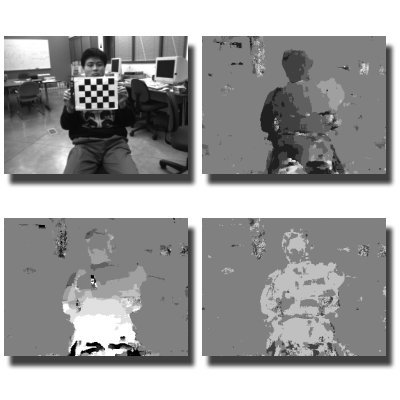

Joint Disparity and Disparity Flow Estimation
This work presents a unified algorithm for estimating both disparity maps and disparity flow, capturing 3D scene motion from a given view. By jointly computing these maps, the method enforces temporal consistency across frames and cross-validates motion information between views.
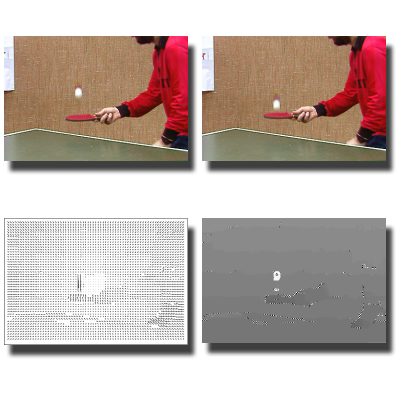
Large Motion Estimation Using Reliability-DP
This work extends a matching-based stereo vision technique to address the large motion estimation problem. The proposed algorithm removes the constant penalty assumption and enforces inter-scanline consistency, enabling dense and reliable optical flow estimation.
Papers: IJCV 2006

Multi-View Stereo Reconstruction
We develop methods that improve multi-view stereo by enhancing matching reliability and producing cleaner, more consistent 3D reconstructions. Together, these techniques strengthen view selection, depth estimation, and point consolidation, enabling more accurate geometry in challenging, occluded, and low-textured scenes.
Subpixel Stereo with Slanted Surface Modeling
This work proposes a stereo matching algorithm that incorporates per-pixel surface orientation to improve depth estimation accuracy. Using an orientation-guided cost aggregation, the method refines results with adaptive support weights and sub-pixel precision.
Papers: PR 2011
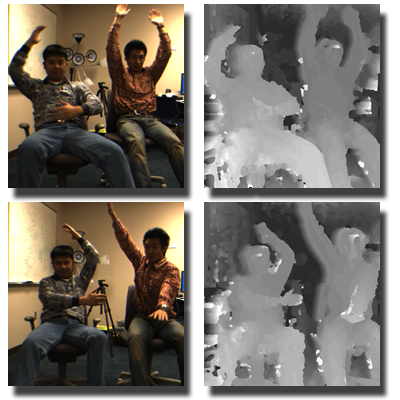

Real-Time Stereo Matching on GPUs
These papers introduce a real-time stereo matching algorithm that efficiently produces reliable disparity maps using a modified dynamic programming framework. By replacing iterative path tracing with local minimum search, the method enables parallel computation on graphics hardware.
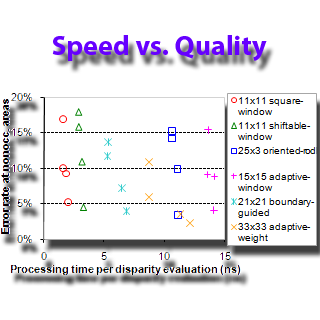
Evaluation of Cost Aggregation Approaches
This work investigates the feasibility of achieving high-accuracy, real-time dense disparity maps using cost aggregation techniques. Six recent cost aggregation methods are implemented and optimized on GPUs, and experimental evaluations demonstrate their effectiveness in balancing speed and accuracy for real-time applications.
Papers: IJCV 2007
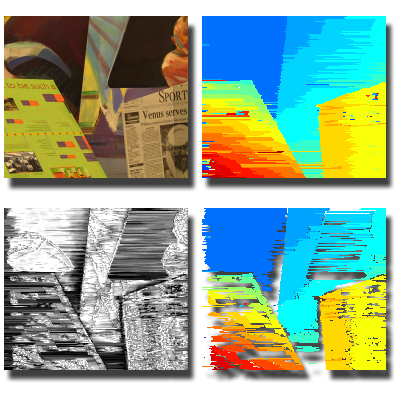
Unambiguous Matching with Reliability-Based DP
We introduce an efficient and unambiguous stereo matching technique that incorporates a novel reliability measure into dynamic programming. The reliability of each match is defined by comparing global disparity assignments that include or exclude it, allowing selectively assigning disparities based on confidence.
Papers: TPAMI 2005, ICCV 2003
Robotics and Artificial Intelligence
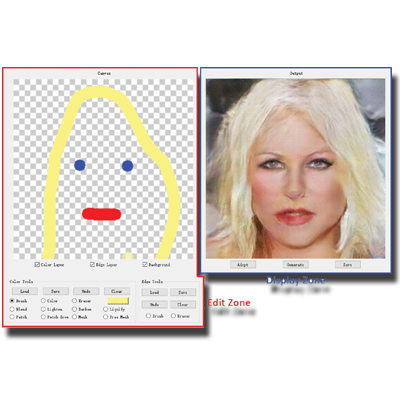
Branched GAN for Scale-Disentangled Learning
A novel multi-branch, scale-disentangled training method is proposed to enable unconditional GANs to learn image representations across multiple scales. This approach enhances the network’s ability to capture both global structure and fine details, benefiting a wide range of image generation and editing tasks.
Papers: TIP 2020

Neural Networks for Arbitrary Style Transfer
Two neural architectures enhance arbitrary style transfer by achieving a stronger balance between structural consistency and stylization quality. Through feature enhancement and iterative refinement, they better preserve semantic content while producing more coherent and visually compelling results.
Papers: AAAI 2020, NeurIPS 2019

Adaptive Dense CNNs
We develop CNN architectures that improve feature reuse and representation efficiency through adaptive aggregation and attention mechanisms. With layer-wise attention, multi-scale aggregation, and stochastic feature reuse, they achieve higher accuracy and reduced overfitting with fewer parameters.

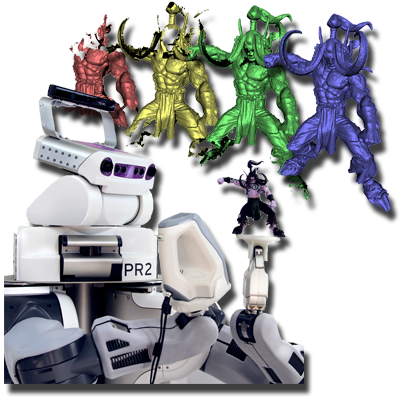
Dual Learning for Image-to-Image Translation
We propose DuelGAN, a dual-GAN framework where two discriminators and generators interact in opposing directions, forming a closed translation loop that enforces consistency. This dueling design enhances training stability, mitigates mode collapse, and improves generation diversity with minimal computational cost.
Papers: ICCV 2017
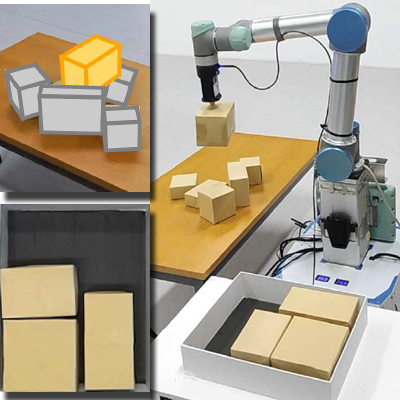
Robotic 3D Packing
We present learning-based solutions for the 3D transport-and-pack (TAP) problem, jointly addressing object transport, placement, and packing. Using reinforcement learning, our neural frameworks encode object geometry and packing states to optimize compactness and efficiency, enabling scalable and generalizable robotic packing.
Papers: SIGGRAPH Asia 2023, SIGGRAPH Asia 2020
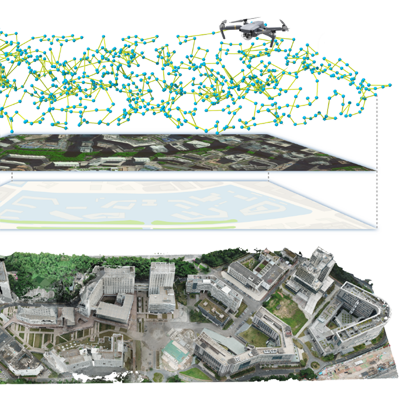
Aerial Path Planning for 3D Reconstruction
We propose adaptive and real-time aerial path planning algorithms for 3D urban scene reconstruction using UAV imagery. Designed to maximize reconstruction quality while minimizing flight time, these methods eliminate the need for prior scene knowledge or multiple site visits, enabling efficient and accessible large-scale urban modeling.
Papers: SIGGRAPH Asia 2021, SIGGRAPH Asia 2020
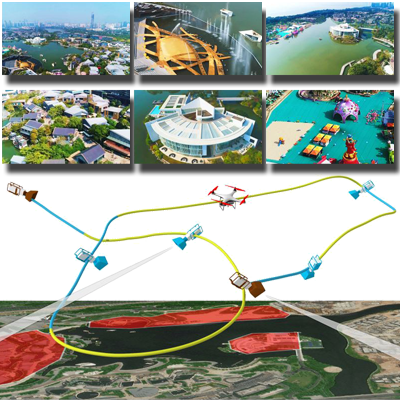
Drone Videography
We develop intelligent camera planning tools that automate the creation of cinematic aerial videos and visual trip summaries. By analyzing scene structure and visual interest, our methods generate trajectories that optimize landmark coverage, composition, and viewer engagement, enabling compelling flythroughs with minimal user input.
Papers: SIGGRAPH 2018, CGF 2016

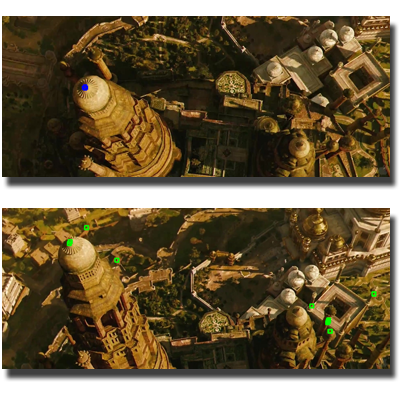
Quality-Driven Autoscanning
We introduce a quality-driven autonomous scanning approach guided by Poisson field analysis. Instead of minimizing scan count, our method selects Next-Best-Views to maximize surface completeness and fidelity, enabling high-quality 3D reconstruction through confidence-guided view planning.
Papers: SIGGRAPH Asia 2014

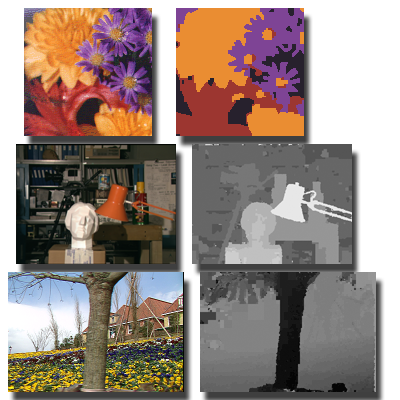
Artificial Multi-Bee Colony Algorithm
We propose an artificial multi-bee-colony (AMBC) algorithm for efficient k-nearest-neighbor field computation, where colonies collaboratively search and share good matches across image patches. This parallel, population-based approach achieves higher accuracy and robustness than existing PatchMatch variants.
Papers: GECCO 2016

Quadtree-based Genetic Algorithm
We propose a quadtree-based genetic optimization framework for vision tasks such as segmentation, stereo matching, and motion estimation. Encoding solutions via quadtrees preserves spatial structure and enables multi-resolution optimization, improving accuracy and robustness.
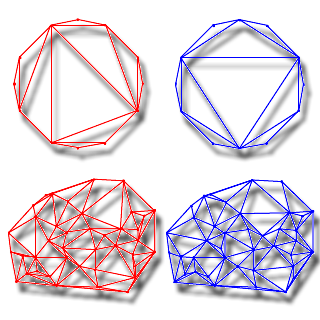
Genetic Algorithm for Minimum-Weight Triangulation
We present a genetic minimum weight triangulation (GMWT) method for planar point sets, introducing polygon-based crossover and adaptive genetic operators. This evolutionary approach outperforms traditional greedy algorithms in producing more optimal triangulations.
Papers: ICEC 1997
